| |
NCRM has its own cell culture and tissue engineering laboratory for research, training and translational work, in which scientists and research staff work to develop various translational application oriented protocols jointly in coordination with clinicians from like minded institutes.
Ophthalmology Hepatology Hemato-Oncology Diabetes Orthopedics
|
| |

A monolayer of human corneal limbal stem cells grown using our technology and materials |
Ophthalmology
We have been able to make the corneal limbal stem cells grow in our synthetic materials Mebiol Gel, which is a Thermogelation polymer. This work is done based on a MoU signed with Vision Research Foundation- Sankara Nethralaya. Once the animal research is completed we intend to take to clinical application, paving a way to cure diseases like persistent corneal ulcer, Stevens-johnson syndrome and chemical and physical injuries to the eye using our invention, which jeopardize the vision of almost 3000 people every year in India.
Apart from the corneal diseases, we have plans to do research on cancer of the eye like retinoblastoma and also curing various retinal disorders using cell therapeutics.
For more details click here |
|
Hepatology
Close to 2 million people in India suffer from acute and chronic liver failure, for which no definitive treatment is available as of now. We have started a joint research with Centre for liver research and diagnostics, Hyderabad to study our materials and technology in curing such diseases using either hepatic progenitor cells or patients own liver stem cells. Initial studies were very promising and we have started the animal studies aiming at finding ways to give a definitive treatment to acute and chronic liver failure. For more details click here |
|
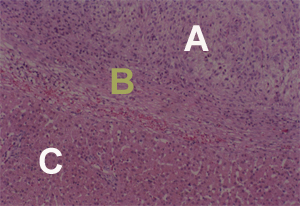
Hepatocytes of a canine model grew in-situ in a cavity filled with Mebiol Gel. The control wheras remained filled with fibrin glue.
|
| |
|
Diabetes Liver stem cells are known to differentiate into insulin secreting cells. Also the native islets of langerhans cells have potentials to multiply, provided a suitable method and material is used. We have a research project exclusively focusing on giving a better treatment to diabetes using cell therapeutics. |
|
Orthopedics
Multiple and compound fractures of the bones leave unhealed or improperly united bone gaps which may warrant bone grafts by another surgery in the bone of the same patient, in spite of which healing takes place taking a long duration of time. We have developed a technology and suitable materials which can allow the faster union of bones and filling of bone gaps by patients own natural bone`s growth. The degeneration of the disc of the vertebral column is yet another problem in orthopedics, in which the centrally located Nucleus pulposus of the disc degenerates leading to compression of the nerves. We have plans to start a research on multiplying patient's own nucleus pulposus cells and reimplantation to treat the intervertebral disc degeneration. |
|
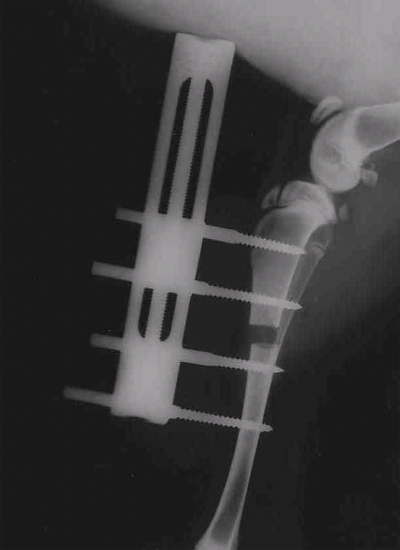 
A surgically created and externally immobilized cavity of a long bone when filled with Mebiol Gel(Capable of supporting osteogenesis) and wrapped around with native periosteum (Left), resulted in bone formation as proven by the calcification (Right) in this 4 weeks X-ray.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
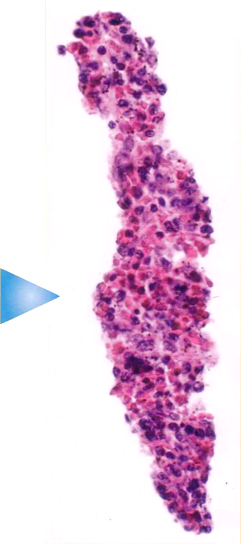
Inflammation of the cartilage of the joints over a period can lead to severe arthritis. The focal articular cartilage defects when occur, we are able to take the same, isolate the normal Chondrocytes and culture in three dimensional form for application in the laboratory. The grown Chondrocytes have more of collagen type II and stain positive with saffronin. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hemato-Oncology
We are now working on various methods to multiply umbilical cord blood cells using our technology and materials so that such expanded UCB stem cells can be stored for future usage and can be donated to HLA mateched donors. As of now though umbilical cord blood expansion is possible, it requires a lot of growth factors and then purifying the same lineage of cells require antibodies. Our aim is to work out a much simpler and cost effective methodology which should be reproducible anywhere.
|
| |
|
| |
*"Nichi" stands for Japan and "In" stands for India. This institute started on an Indo-Japan collaboration now has spreaded further with global alliances |






